Climate justice means ensuring that environmental actions are fair and include everyone, especially those most impacted but least responsible. You should recognize that marginalized communities and poorer nations often face the worst effects like flooding and pollution, despite emitting less. Effective approaches prioritize fairness, inclusive decision-making, and systemic change. If you want to understand how policies and community efforts can create true equity in tackling climate change, keep exploring these vital ideas.
Key Takeaways
- Climate justice emphasizes fairness by recognizing that marginalized communities face disproportionate impacts despite minimal emissions contributions.
- Policies should prioritize vulnerable populations through distributive and procedural justice, ensuring inclusive decision-making processes.
- Addressing systemic inequalities involves dismantling barriers and holding corporations accountable for environmental damage.
- Empowering local and indigenous communities fosters resilience and ensures their voices influence climate solutions.
- Intergenerational equity calls for policies that protect the rights of future generations alongside current populations.
Understanding the Foundations of Climate Justice

What are the core ideas that underpin climate justice? At its heart, climate justice focuses on fairness in how climate change impacts different communities. It emphasizes that those least responsible for emissions often suffer the worst effects, highlighting the need for equitable treatment. Central principles include human rights, equality, and inclusive decision-making, ensuring marginalized groups have a voice. It also recognizes the historical responsibilities of industrialized nations and fossil fuel industries in causing climate change. Climate justice calls for fair distribution of both burdens and benefits, addressing social and environmental disparities. By advocating for systemic change, it aims to protect vulnerable populations from climate harms while holding major polluters accountable. Additionally, understanding the importance of environmental considerations is crucial for sustainable solutions. Ultimately, climate justice seeks social and environmental equity in climate action.
Disparities in Emissions and Impact

Despite contributing the least to greenhouse gas emissions, marginalized communities and poorer nations often bear the brunt of climate impacts. You might live in a low-income neighborhood that faces frequent flooding, extreme heat, or toxic pollution, even though your community contributes minimally to greenhouse gases. Meanwhile, wealthier regions emit half of the world’s emissions but suffer less immediate harm. Indigenous peoples, communities of color, and the Global South experience disproportionate health, economic, and environmental damages. These disparities reveal a “triple injustice”: being most affected, contributing least, and facing harmful policies. Climate impacts deepen existing inequalities, making it clear that those least responsible for emissions often carry the heaviest burdens, highlighting the urgent need for equitable solutions that prioritize vulnerable populations. Automation technologies are increasingly being employed in climate adaptation efforts to improve disaster response and resource management.
Frameworks for Equity and Fairness

Frameworks for equity and fairness in climate justice provide essential principles to guarantee that the burdens and benefits of climate action are shared justly. You need to understand that these frameworks prioritize distributive justice, ensuring marginalized communities receive support proportional to their vulnerability and historical exclusion. Inter-generational equity reminds you that current decisions affect future generations, so fairness extends beyond today. Intra-generational equity emphasizes addressing disparities among people living now, focusing on resource access and resilience. Procedural justice calls for inclusive decision-making, giving marginalized groups a voice in climate policies. When applied, these frameworks help you create policies that promote social cohesion, reduce inequalities, and foster equitable climate resilience, ensuring everyone benefits from sustainable solutions. Incorporating AI-powered virtual reality in e-learning can further support educational outreach and awareness efforts on climate justice issues.
Addressing Environmental Injustices Through Policy

How can policies effectively confront environmental injustices and promote equity? You can implement laws that prioritize marginalized communities, ensuring they receive fair protection and resources. Policies must target the root causes of inequality, such as dismantling systemic barriers that limit access to clean air, water, and land. Funding green infrastructure projects in vulnerable areas helps reduce exposure to pollution and climate impacts. You should promote inclusive decision-making processes, giving marginalized voices a seat at the table. Legislation that holds corporations accountable for environmental damage is vital, as is ensuring climate mitigation costs are fairly distributed. By embedding equity principles into policy frameworks, you create a system that not only addresses injustices but also empowers communities most affected by climate change. Understanding the role of environmental justice in shaping effective policies is essential for creating sustainable and equitable solutions.
Mobilizing Communities for Equitable Climate Action
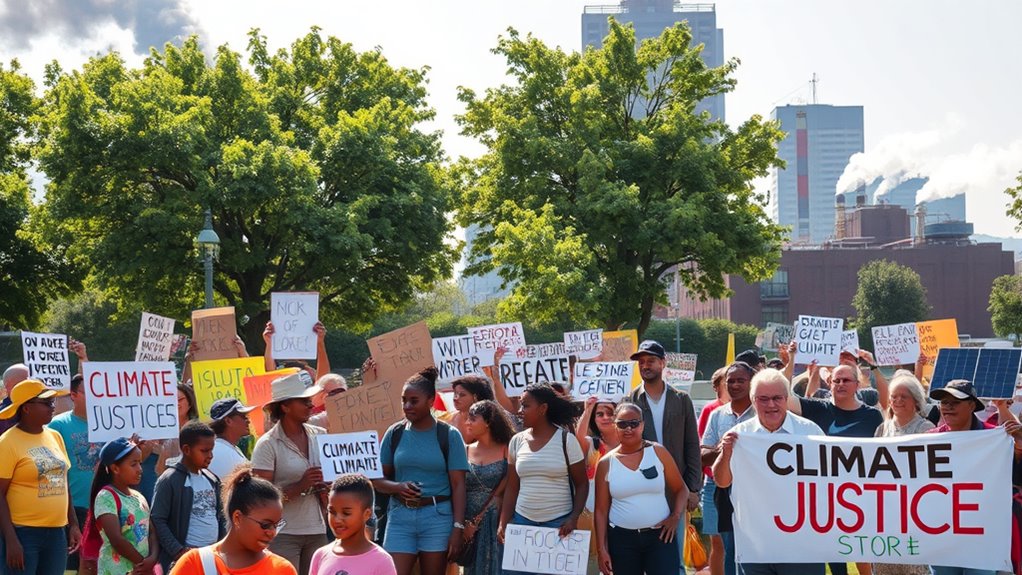

Mobilizing communities is essential for achieving equitable climate action because it guarantees that those most affected by climate change have a voice in shaping solutions. When you empower local groups, you promote inclusive decision-making and assure policies address real needs. Imagine a table illustrating community efforts:
| Community Action | Focus Area | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Grassroots Groups | Education | Raising awareness |
| Local Leaders | Policy | Influencing decision-makers |
| Youth Movements | Advocacy | Demanding change |
| Indigenous Tribes | Land Rights | Protecting territories |
Additionally, understanding the importance of public engagement can significantly enhance the effectiveness of climate initiatives by ensuring diverse perspectives are included in decision-making processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Climate Justice Principles Influence International Climate Negotiations?
You see that climate justice principles shape international climate negotiations by emphasizing fairness and inclusivity. They push you to advocate for marginalized nations and vulnerable communities, ensuring their voices are heard in decision-making. You recognize the need to address historical emissions from industrialized countries and promote equitable sharing of climate responsibilities and benefits. These principles motivate you to push for policies that respect human rights and prioritize social equity in global climate efforts.
What Role Do Indigenous Communities Play in Climate Justice Efforts?
You play a crucial role in climate justice efforts by advocating for indigenous rights, sharing traditional knowledge, and pushing for inclusive policies. Your communities often face disproportionate climate impacts despite minimal contributions to emissions. By participating in protests, legal actions, and negotiations, you help guarantee your voices are heard, and your land and resources are protected. Your leadership drives equitable solutions that honor cultural heritage and promote sustainable, community-led climate resilience.
How Can Economic Policies Better Support Vulnerable Populations Facing Climate Impacts?
You can help vulnerable populations facing climate impacts by pushing for economic policies that put their needs front and center. This means advocating for fair investments in adaptation, affordable healthcare, and resilient infrastructure. It’s about giving them a seat at the table and ensuring resources are shared fairly. When policies are equitable, they can bridge the gap, making sure no one is left holding the bag in climate crises.
What Challenges Exist in Implementing Equitable Climate Adaptation Strategies?
You face challenges like limited resources and political resistance when trying to implement equitable climate adaptation strategies. Funding often prioritizes immediate needs over long-term equity, making it hard to support vulnerable communities effectively. Additionally, systemic inequalities and lack of inclusive decision-making hinder fair distribution of adaptation efforts. You must also surmount resistance from powerful industries and navigate complex policy landscapes to ensure marginalized groups receive the protection and support they deserve.
How Do Climate Justice Initiatives Intersect With Broader Social Justice Movements?
You might think climate justice is just another trendy hashtag, but it actually intersects deeply with broader social justice movements. By fighting for marginalized communities‘ rights, you push for systemic change that addresses inequality in both environmental and social spheres. Your activism highlights how climate impacts mirror social disparities, demanding a united front—because if we ignore these links, we’re just adding fuel to the fire of injustice, not dousing it.
Conclusion
As you consider the path forward, remember that true climate justice isn’t just about policies or protests—it’s about the unseen forces shaping who bears the burden. Will you stand for a future where everyone’s voice matters, or watch disparities deepen? The choices you make today could determine whether justice prevails or is lost in the shadows. The question isn’t just what’s fair—it’s what kind of world you’re willing to create.